March 28, 2017 k-2-math-practices, k-2-geometry
How to Use the Standards for Mathematical Practice in K– Grade 2
By: Jeff Todd
One way to help students achieve high levels of mathematical proficiency is to use the Standards for Mathematical Practice in addition to content standards. When we are able to infuse our lessons with these practices, students engage their higher order thinking skills in order to solve problems.

As I work with other teachers, they often struggle to use the Standards for Mathematical Practice within the different content domains: geometry, number sense and operation, measurement, data, statistics, ratio and proportion, algebra, algebraic thinking, equations, expressions, and functions.
This post is the first in a new series on these practices and how to apply them to the content domains at different grade levels.
You could use the ideas in this post and its associated download to plan your lessons, or as the basis for a professional development session for your math teachers.
In early elementary geometry, there are three clusters of activities that can help you to infuse your lessons with the Standards for Mathematical Practice.
Sorting shapes, composing and decomposing figures, and modeling real life using geometry are excellent ways to engage your students in these practices, while promoting higher order thinking as you teach.
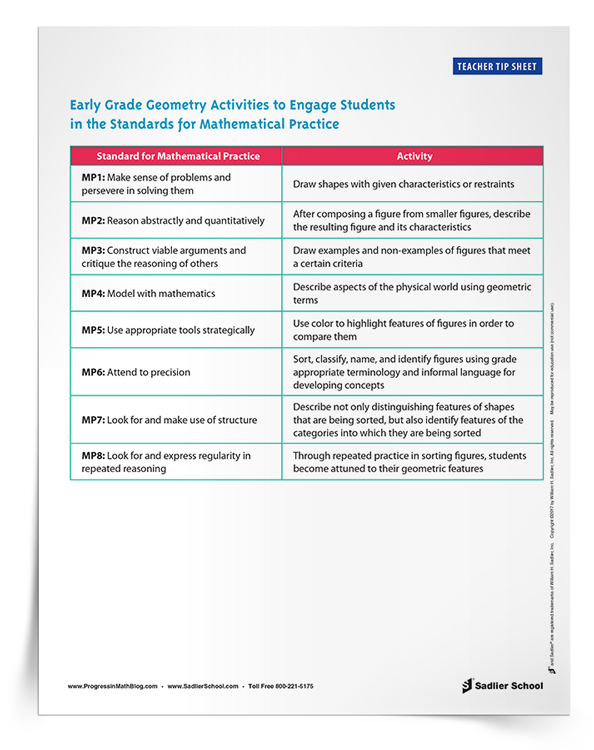
In addition to the ideas presented below, you can download a list of the practices and early elementary activities to use for each Standard for Mathematical Practice.
ACTIVITY #1: SORTING FIGURES
At the early grade levels, sorting and categorizing figures is one of the best opportunities for students to use the Standards for Mathematical Practice in geometry for the early grades.
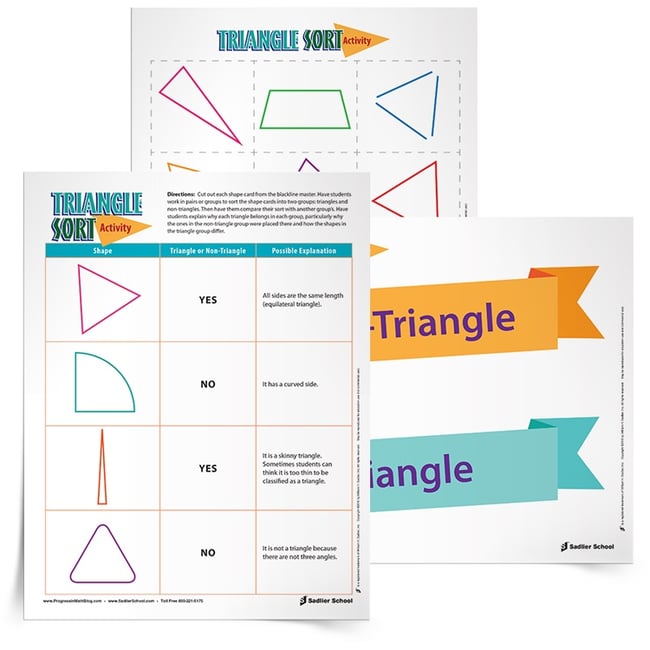
Students use Mathematical Practice 3 (MP3, Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others) when they tell which category a figure belongs to and explain why. Students can also address this practice by creating examples and non-examples of figures that belong to a category.
When students are thinking about the structure of the figures they are sorting, they are using MP7 (Look for and make use of structure). They might think about the number of sides, the length of sides, whether there are right angle or curves, and whether figures are open or closed. Through repeated experiences using different kinds of sorts, they are able to create generalizations about shapes and use MP8 (Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning).
As students explain the reasons that a figure belongs in a category or not, they use geometric vocabulary to justify their choices.
When students question each other they use MP6 (Attend to precision) while they refine their thinking and focus on the distinguishing attributes needed to place a figure in one category or another.
Many variations of sorting related to categorizing shapes are also useful in promoting the Standards for Mathematical Practice. For instance “Guess My Rule” is an activity where students look at a group of figures and try to figure out what category they might be in. This is a way to engage students in MP1 (Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them).
BONUS: Download my Triangle Sort Activity to use with students!
ACTIVITY #2: COMPOSING/DECOMPOSING SHAPES
A second activity which students engage in from Kindergarten to Grade 2 is composing and decomposing shapes. This has been more extensively discussed in a previous blog post.
What I want to highlight here is how composing and decomposing shapes relates to the Standards for Mathematical Practice.
When composing and decomposing figures, students can engage in MP5 (Use appropriate tools strategically) as they choose a strategy to solve a problem. Should they use tangrams, pattern blocks, attribute blocks, grid paper, plain paper, scissors, toothpicks, or other manipulatives? Can they use color in their drawings to help focus attention on important features? Do they know of apps or computer software they can use to solve the problem?
The tools and strategies they choose are evidence of how they are using MP1 (Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them).
One challenging area for many students is seeing how several pieces can be composed into a new shape, and that this new shape can have characteristics of its own, independent of the shapes that compose it (for instance, using two congruent triangles to form a parallelogram). This flexibility in thinking abstractly about objects is one of the features of MP2 (Reason abstractly and quantitatively).
BONUS: Download these Number Bond Poetry Frames to use with your students that focus on composing and decomposing numbers.

ACTIVITY #3: MODELING REAL LIFE
The last type of activity you can use to engage students in the Standards for Mathematical Practice is to relate geometry to the physical world.
MP4 (Model with mathematics) has become a major focus of open response standardized test items, and students should be provided with as many opportunities as possible to relate math to common situations around them. At the early grades in geometry questions such as, “Where do we see triangles in the world around us?” help students connect mathematics to their lives.
When students are seeing mathematical figures in the physical world, they are using MP7 (Look for and make use of structure).
Their ability to apply abstract ideas about shapes to the physical world and vice versa is evidence of MP2 (Reason abstractly and quantitatively) and will help them to create representations of word problems in their future math courses and on the job.
IN SUMMARY
These three types of activities—Sorting Figures, Composing and Decomposing Shapes, and Modeling Real Life—are ways that you can implement the Standards for Mathematical Practice and tap into students’ higher order thinking while they learn geometry.
If you are looking for ways to incorporate the Standards for Mathematical Practice into your lessons, download the Teacher Tip Sheet and keep it in your planning book while you are teaching geometry.